Adulterated Drug Test FAQ
ADULTERANTS IN DRUG TESTING
People will go to extremes to disguise their drug use.
Whether it's a potential job applicant, an existing employee, or a rehab inpatient, adulteration is a reality of using drug tests.
Thanks to advancements in clinical research, adulterated specimens can be instantly detected with easy-to-use adulteration strips.
Some drug tests even provide built-in adulteration testing, so you never have to worry about being fooled by a cheater.
What is adulteration?
Adulteration is the tampering of a urine specimen with the intention of altering drug test results. The use of adulterants can cause false negative results in drug tests by either interfering with the screening test and/or destroying the drug metabolites present in urine. Urine adulteration can be performed in many ways:
- Drinking excessive amounts of water before a urine drug test
- Taking creatine supplements to trigger false positives via creatinine metabolite
- Submitting “synthetic urine” from a foreign donor
- Dilution using sink or toilet bowl water
There are no true ways to pass a drug test apart from practicing sobriety. A modern-day urine drug screen provides drug test adulteration detection by measuring urinary properties:
- Creatinine
- pH
- Specific Gravity
- Glutaraldehyde
- Nitrites
- Oxidants/Pyridinium Chlorochromate (PCC).
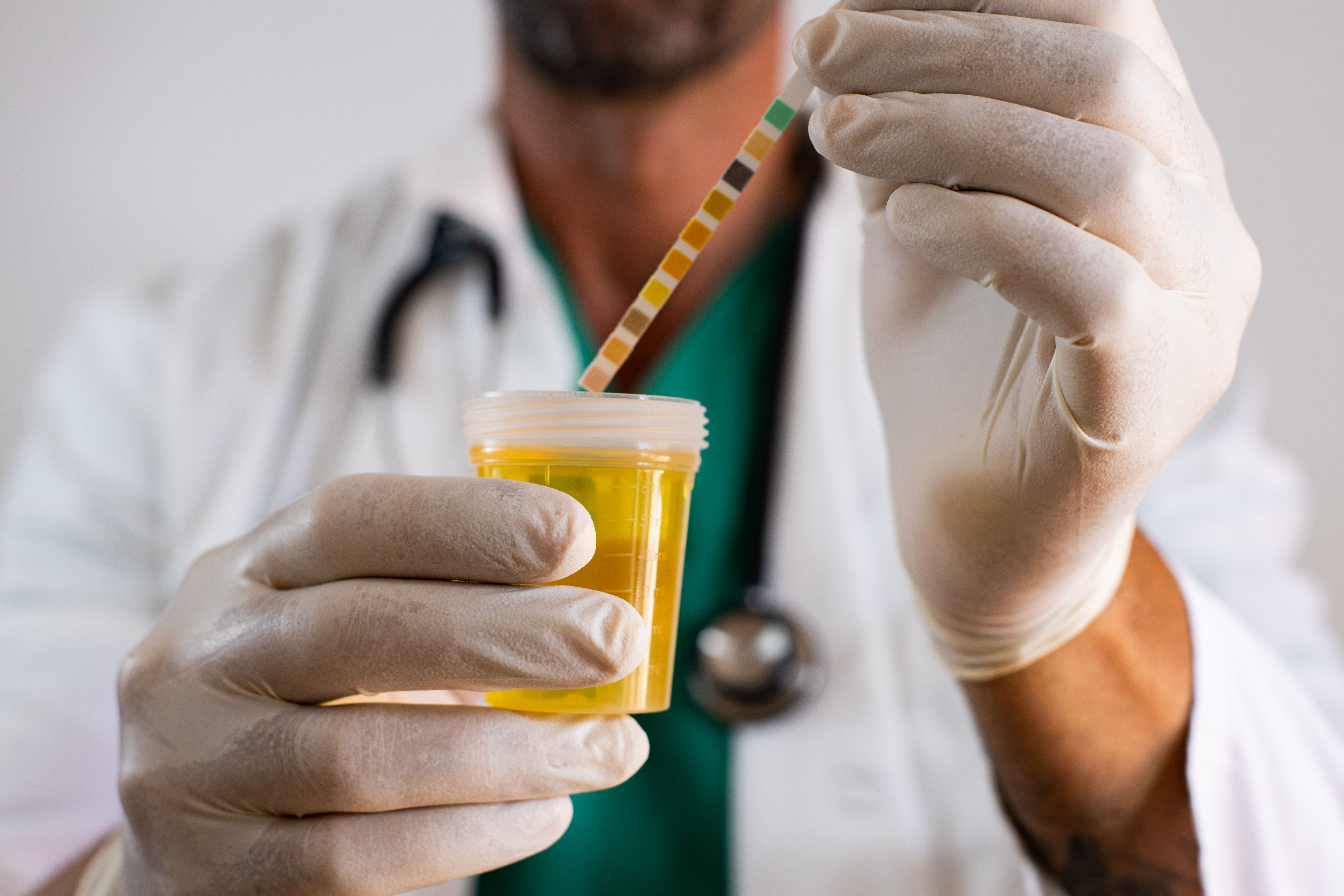
What are normal urine pH levels and how does urine pH indicate drug test adulteration?
A normal urine pH level hovers around 6.0, which means urine samples should be slightly more acidic than water. Water is neutral at pH 7.0. A diluted urine sample can be identified when the urine pH level is measured close to neutral. Adulterating urine with acidic compounds, e.g. vinegar and lemon juice, or basic compounds, e.g. bleach and creatine will bring normal urine pH levels outside of the normal range.
How do you read the temperature strip on urine drug test kits?
Ensure the temperature strip is black before administering a urine drug test. Once urine is deposited into the drug test cup, the black temperature strip will become a bluish green color. Normal urine temperature falls between 97 and 100 degrees. As a reference, 98.6 degrees is average body temperature. If urine specimen temperature is indicated outside of the normal urine temperature range, the drug test result should be Invalid. Many drug testing adulteration methods, e.g. using synthetic urine or swapping clean urine may not affect the temperature of urine specimens. Therefore, temperature should not be the only factor used to determine possible adulteration.
How does the oxidants/PCC drug test panel check for drug test adulteration?
When included in a drug test, oxidants/pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) can detect the presence of adulterants, specifically bleach and hydrogen peroxide. Pyridinium chlorochromate (also sold as “UrineLuck”) is a commonly used adulterant; however, normal urine specimens should not contain any traces of PCC.
What is glutaraldehyde? Is it an indicator for a tampered result?
Glutaraldehyde tests for the presence of an aldehyde. Adulterants containing glutaraldehyde may cause false negative drug test results by disrupting the enzyme used in some immunoassay screens. Unadulterated urine specimens should not contain any traces of glutaraldehyde.
What is specific gravity?
Specific gravity tests for dilution for a urine specimen. The average specific gravity of urine specimens ranges from 1.003 to 1.030g/cm³. Values outside this range suggest sample adulteration by dilution with water or other liquid compounds.
How is nitrite measured for adulteration?
Nitrite tests for adulterants which work by oxidizing carboxy-tetrahydrocannabinol, the body’s primary metabolite of marijuana. Normal urine specimens should not contain nitrate, and the presence of nitrates immediately flag the possibility of adulteration.